US Case 2: Posterior Interosseus Nerve (PIN) and the Arcade of Fröshe Entrapment
Introduction:
The PIN is a branch of the radial nerve that provides motor innervation to the extensor compartment of the forearm. It passes between the two heads of the supinator muscle through the arcade of Fröshe distal to the radial head.
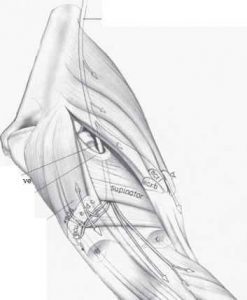
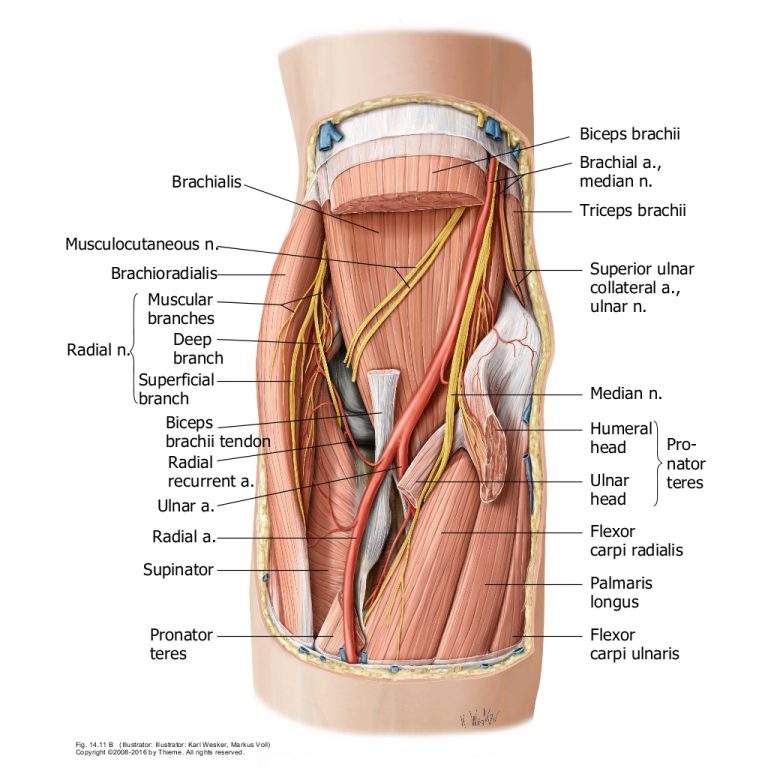
It then passes over abductor pollicis longus muscle origin to reach interosseous membrane and transverses along the posterior interosseous membrane to provide motor innervation to:
Common extensors
ECRB (maybe from radial nerve proper), Extensor digitorum communis (EDC), Extensor digiti minimi (EDM), Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
Deep extensors
Supinator, Abductor pollicis longus (APL), Extensor pollicus brevis (EPB), Extensor pollicus longus (EPL), Extensor indicis proprius (EIP)
The nerve also provides sensory fibres to the dorsal wrist capsule via a terminal branch which is located on the floor of the 4th extensor compartment. It provides no cutaneous innervation.
Clinical Presentation:
Insidious onset, maybe misdiagnosed as a ‘tennis elbow’.
Pain in the elbow and forearm with possible referral to the wrist.
Weakness of the fingers, wrist and thumb.
On examination there may be atrophy of the forearm extensor muscles with chronic compression of the nerve.
Weakness noted with resisted wrist extension.
Resisted supination may elicit symptoms.
Probe position:
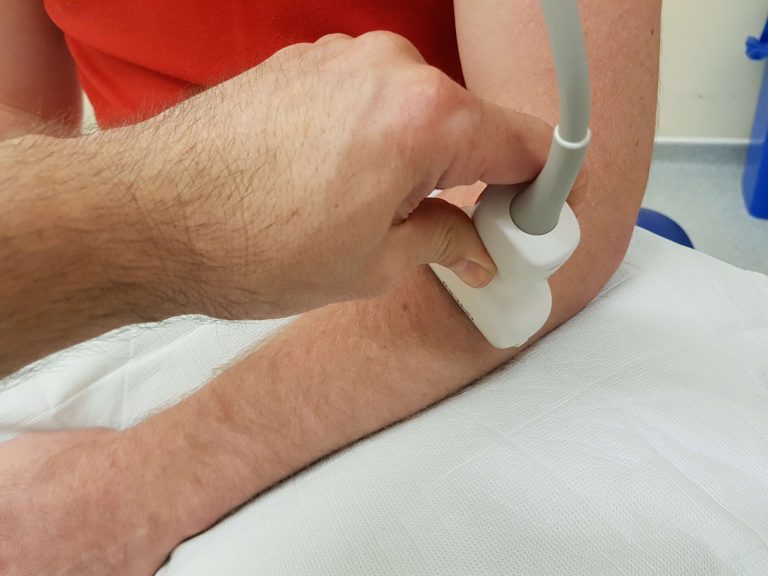
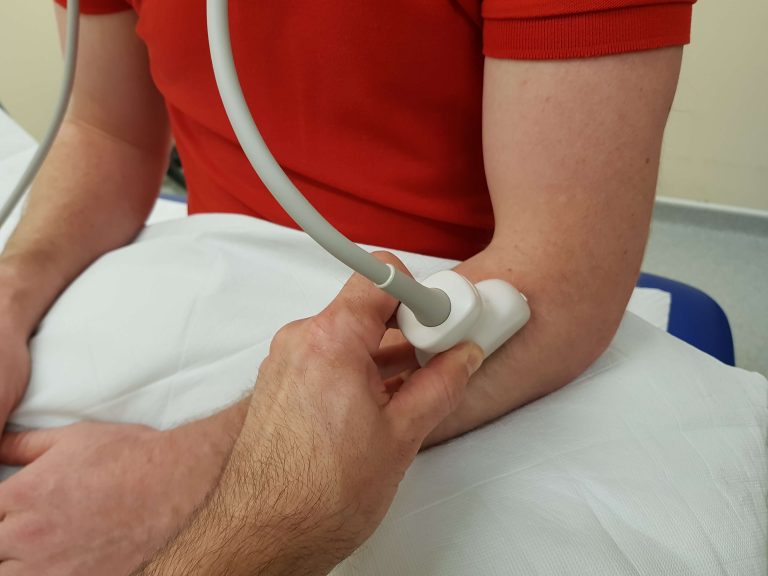
US image:
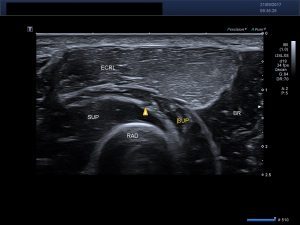
Transverse image of the lateral aspect of the proximal forearm. ECRL-extensor carpi radialis longus, SUP-supinator, RAD-radius, Arrowhead-PIN
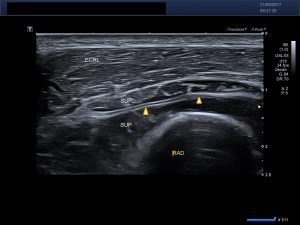
Longitudinal image of the lateral aspect of the proximal forearm. ECRL-extensor carpi radialis longus, SUP-supinator, RAD-radius, Arrowhead-PIN
